In today’s world, there are many solutions for producing pure water, including distillation, absorption, reverse osmosis, etc., but the most economical and principled method is the reverse osmosis system.
Reverse osmosis is a process in which pressure is used to reverse the osmotic flow of water through a semipermeable membrane. If a semipermeable membrane is placed between two solutions of pure water and impure water, water flows naturally and under osmotic pressure from a lower concentration to a higher concentration. The membrane is usually made of cellulose acetate or polyamide. However, today the membrane is made of a mixture of cellulose acetate and cellulose triacetate. The natural direction of movement of the solvent is such that the more concentrated solution is diluted.
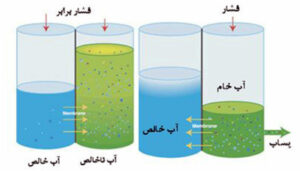
In the figure below, pure water passes through the membrane and enters the impure water. If the system is allowed to reach equilibrium, then the level of the salt water (water containing impurities) will rise above the level of the pure water. This difference in level on both sides of the membrane is called osmotic pressure. In fact, only water molecules are able to pass through the semipermeable membrane.
According to the figure:
Left: Water molecules in the pure water section enter the impure water chamber due to the natural phenomenon of osmosis.
Right: By applying a pressure P higher than the osmotic pressure, water molecules can be forced to enter the pure water chamber from the salt water chamber. This is the same concept as reverse osmosis and is a way to prepare fresh water from salt water.
Therefore, by applying mechanical pressure to salt water, water molecules are separated from salt molecules (impurities). This process is called reverse osmosis.
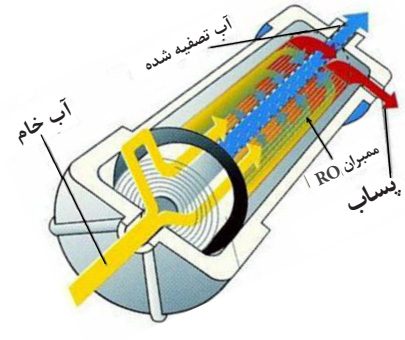
After passing through the primary filters (pre-filters) and performing initial purification, raw (untreated) water enters the housing chamber containing the RO membrane with pump pressure. The amount of wastewater in different systems is different. But usually the ratio of the system’s effluent to its production is three to one. In other words, at the beginning of the system’s operation, for every one unit of purified water, three units of water will enter the wastewater. Reverse osmosis can remove thousands of organic and inorganic contaminants from water. This system is designed to eliminate chlorine taste and odor, rust, scale, and other common concerns about public water by reducing or completely eliminating arsenic, asbestos, chromium, fluoride, lead, mercury, volatile organic compounds, THMs, Giardia, and Cryptosporidium.
Components of modern pure water systems
Today, due to the existence of different devices and the possibility of selection, the design of a pure water production system in factories can be different, but the common design includes the following main components:
1 – UV lamp uses ultraviolet light to disinfect and remove chlorine-resistant microbes.
2 – 50 micron cartridge filter Cartridge filters are one of the most common filters due to their high filtration efficiency and absorption of colloidal particles, salts and sediment with an absorption accuracy of 5 to 20 microns compared to sand filters (with an absorption accuracy of 30 to 60 microns), their economic price and the fact that the cartridge can be washed.
3- Hardener: The performance of resin hardeners is defined by replacing the negative hard ions in hard water with the positive sodium atom present in the resin in the hardener, which in this way removes water hardness. Hardeners are usually made of two types: steel and FRP.
4- A heat exchanger is a device used to transfer heat efficiently from one environment to another. Heat exchangers transfer heat between two or more fluid streams flowing within the device.
5- The membrane consists of several layers of semi-permeable membranes wrapped around a central tube and impurities are not able to pass through the membrane, so on one side of the membrane there will be almost pure water that will flow into the central tube and be directed towards the purified water outlet. On the other side of the membrane layers, there will be water concentrated from impurities that will be directed towards the sewage system.
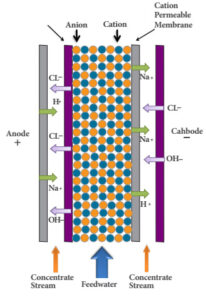
6- Electrodeionizer: Electrodeionization is an electrochemical process in which polymer membranes containing ion exchange resins are used. These resins are coated on polymer membranes such as polyethylene.
Cation membranes are permeable to cations, and anions can also pass through anion membranes. By connecting the anode and cathode electrodes to a direct current source and establishing an appropriate potential difference, an electric field is created between the electrodes, and the resulting driving force causes the cations to move towards the cathode and the anions to move towards the anode. The electric field, due to the decomposition of water, causes the formation of hydrogen and hydroxyl ions, which in turn cause the regeneration of the ion exchange resins.